Chapter 10: Design a Notification System
What is a notification system?
A notification system is used to send notifications to users via different channels.
Problem Understanding & Scope
- Types of Notifications Supported
- Real-time Requirement
- Supported Devices
- Notification Trigger Mechanisms
- User Opt-out Capability
- Scale and Volume
Types of Notifications Supported
What types of notifications are supported?
- Push Notifications
- SMS Notifications
- Email Notifications
Real-time Requirement
The system is defined as a "soft real-time system". It means that the goal is to send notifications as soon as possible, but not necessarily within a specific time frame.
Supported Devices
What devices are supported?
- iOS
- Android
- Web
Notification Trigger Mechanisms
What notification trigger mechanisms are supported?
- client applications
- server-side scheduling
User Opt-out Capability
User should be able to opt-out from notifications.
Scale and Volume
Daily volume of notifications:
- 10 million mobile push notifications.
- 1 million SMS messages.
- 5 million emails.
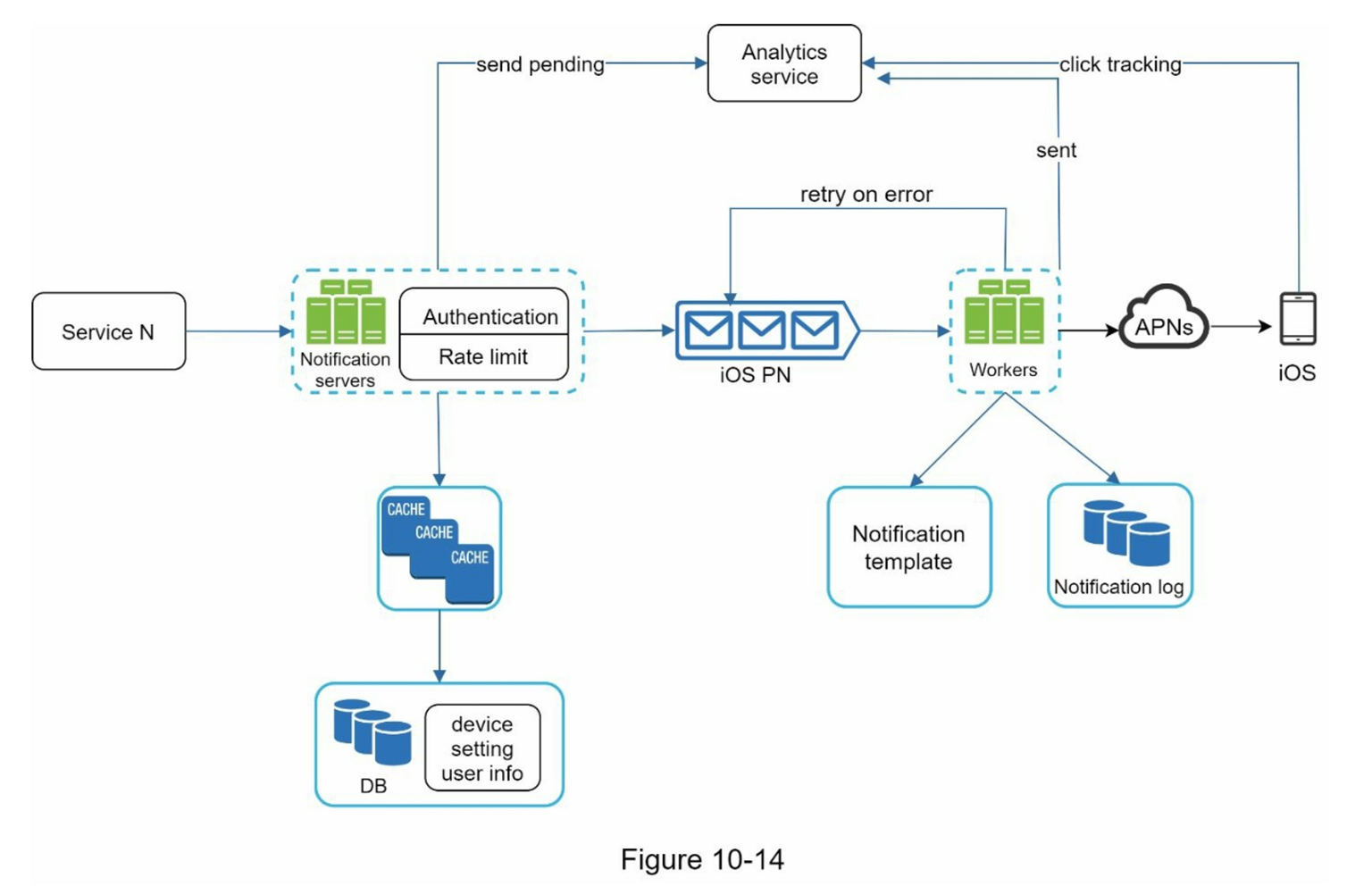
High-Level Architecture
Different Types of Notifications
iOS Push Notification
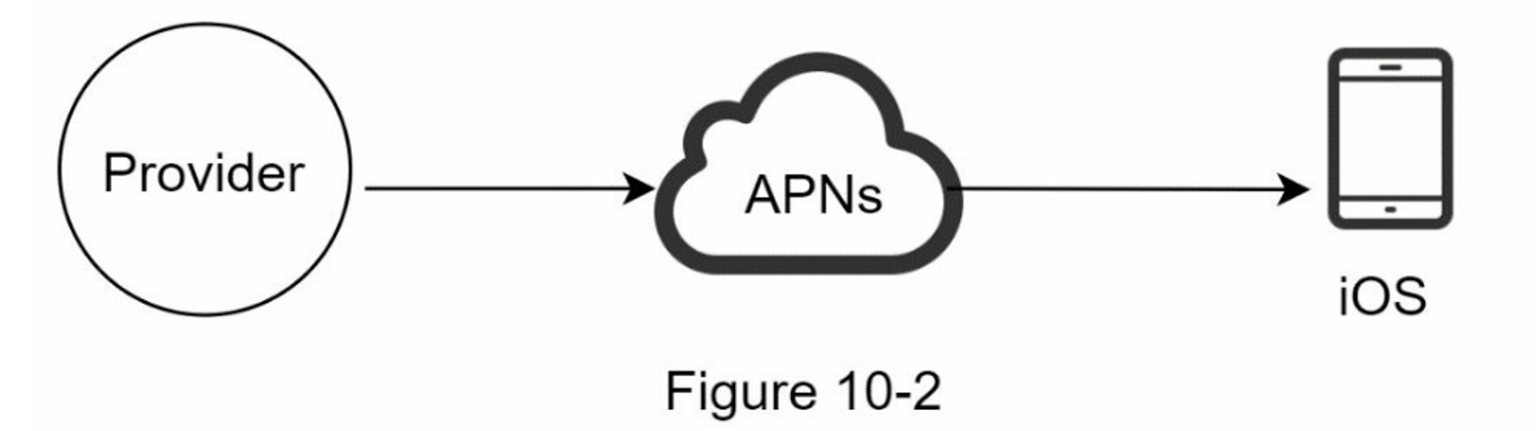
To send iOS push notifications, there are three parties involved:
- Provider
- APNS (Apple Push Notification Service)
- Device
What does the Provider do?
The Provider needs to build a notification payload and request APNS to send it to the Device.
Example payload:
{
"aps": {
"alert": {
"title": "Order Confirmation",
"body": "Your order has been confirmed"
},
"badge": 1
}
}
What does the APNS do?
The APNS receives the notification payload from the Provider and sends it to the Device.
What does the Device do?
The Device receives the notification from the APNS and displays it to the user.
Android Push Notification
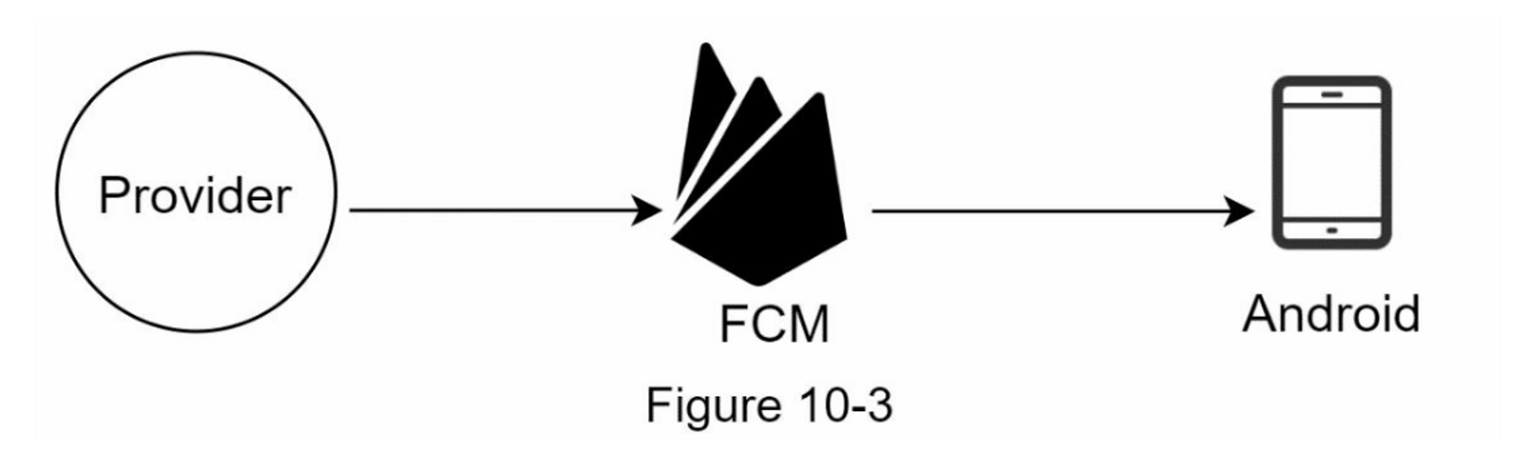
To send Android push notifications, there are three parties involved:
- Provider
- Firebase Cloud Messaging (FCM)
- Device
SMS Notification
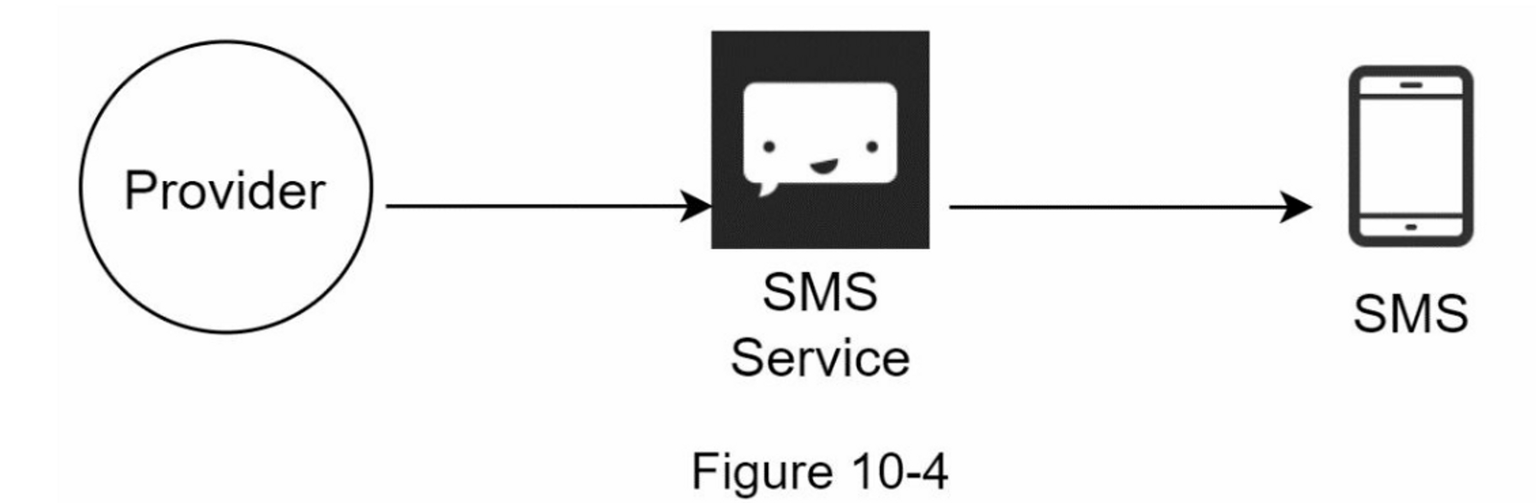
To send SMS notifications, there are three parties involved:
- Provider
- SMS Service
- Device
Email Notification
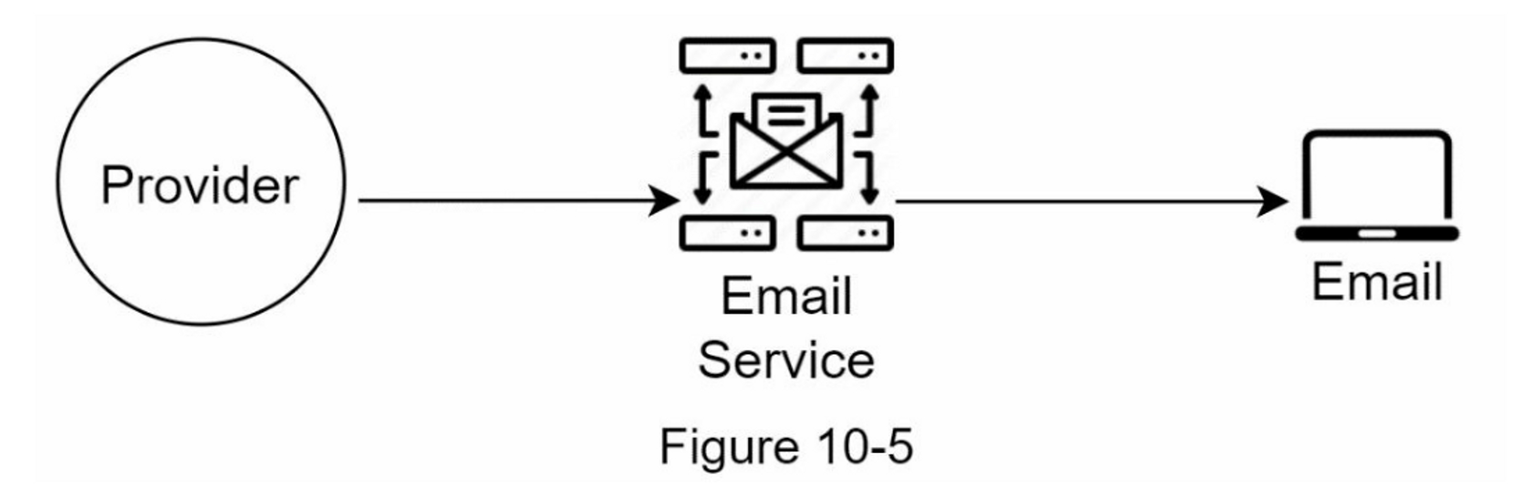
To send email notifications, there are three parties involved:
- Provider
- Email Service
- Device
Integration with Third-Party Services
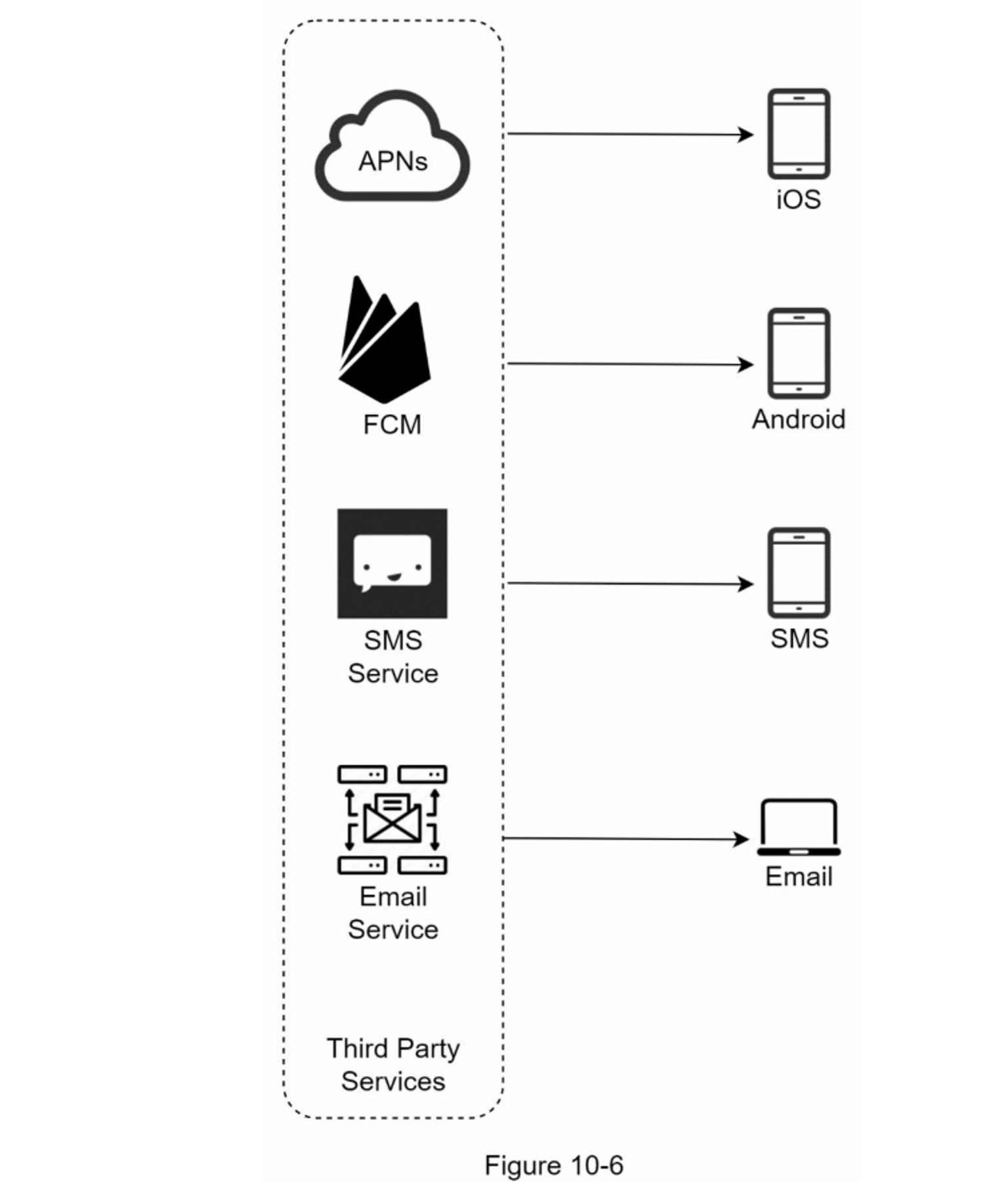
How to send notifications to different devices?
- Device Token Collection
- Process of Sending/Receiving Notifications
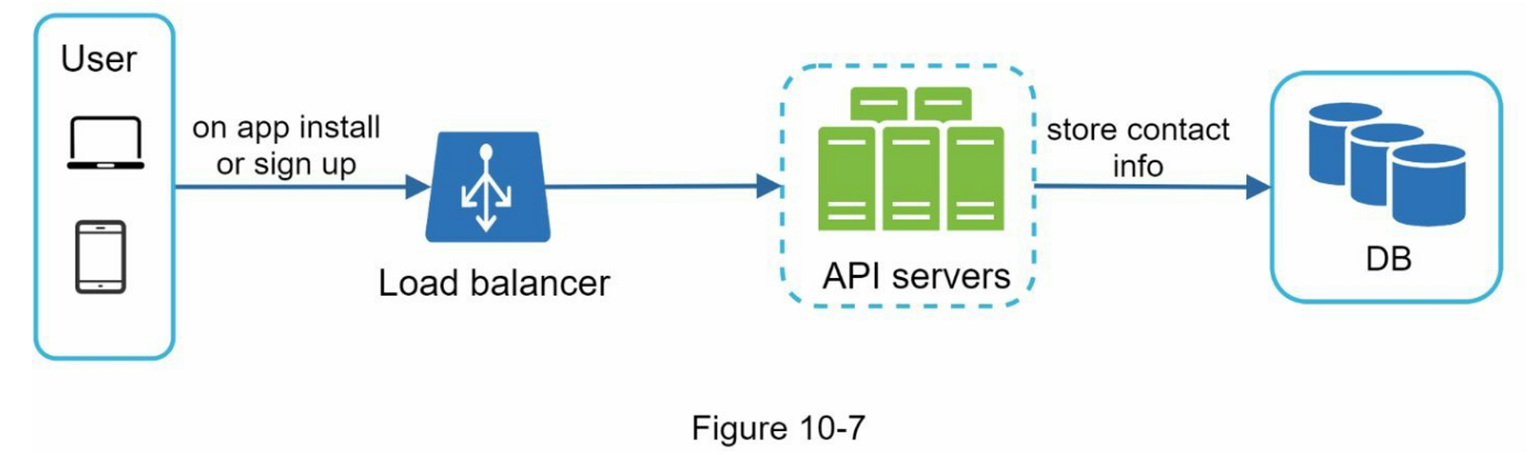
Device Token Collection
To send notifications to different devices, we need to collect the device tokens from the devices and store them in the database.
Process of Sending/Receiving Notifications (Initial Design)
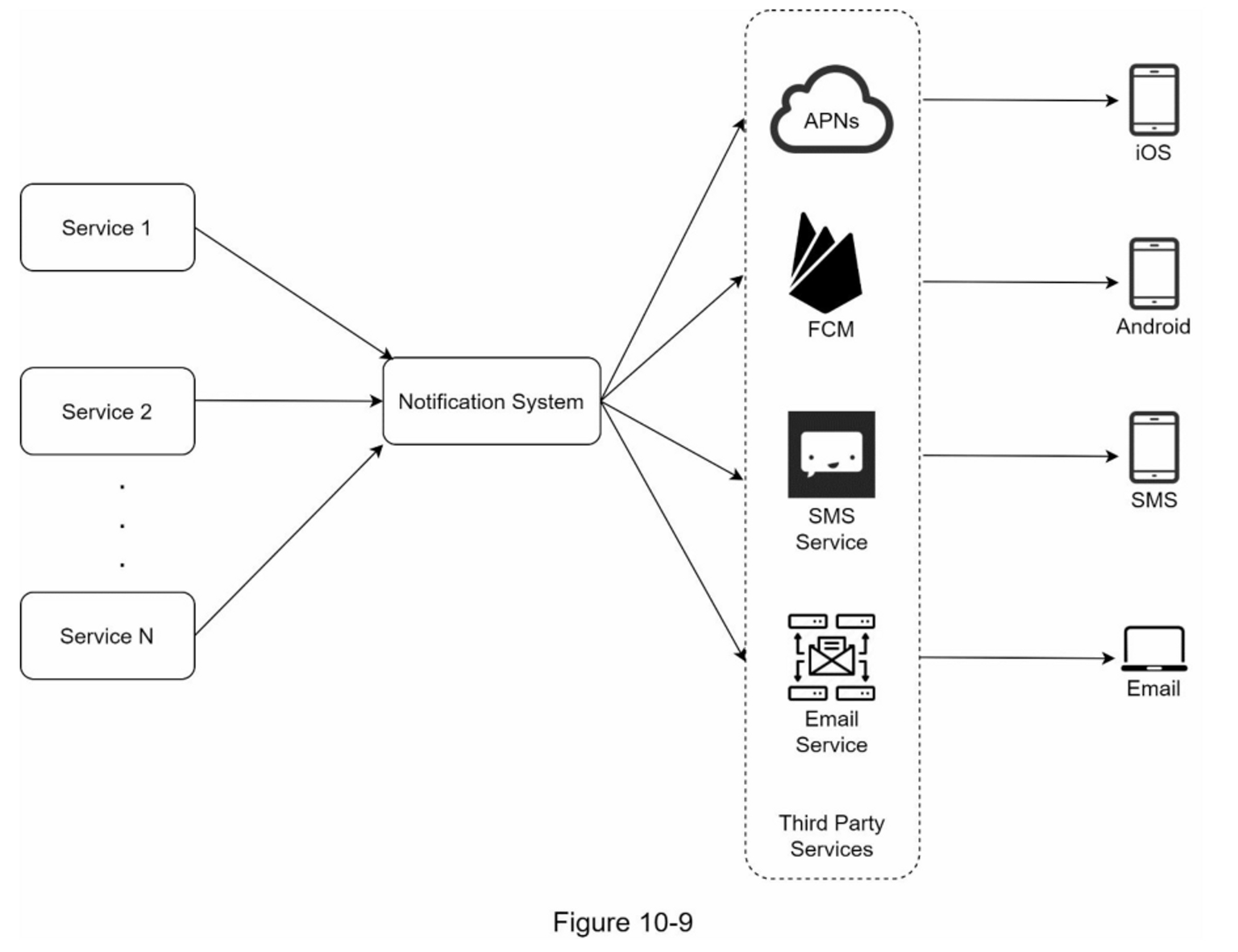
- Services 1 to N (e.g., microservices, cron jobs, distributed systems) trigger notification events.
- Notification Service receives the notification events and sends them to the third-party service.
- Third-Party Service sends the notification to the User Device.
- User Device (iOS, Android, SMS, Email) receives the notification.
Process of Sending/Receiving Notifications (Improved Design)
- Move the database and cache out of the notification server.
- Add more notification servers and set up automatic horizontal scaling.
- Introduce message queues to decouple the system components.
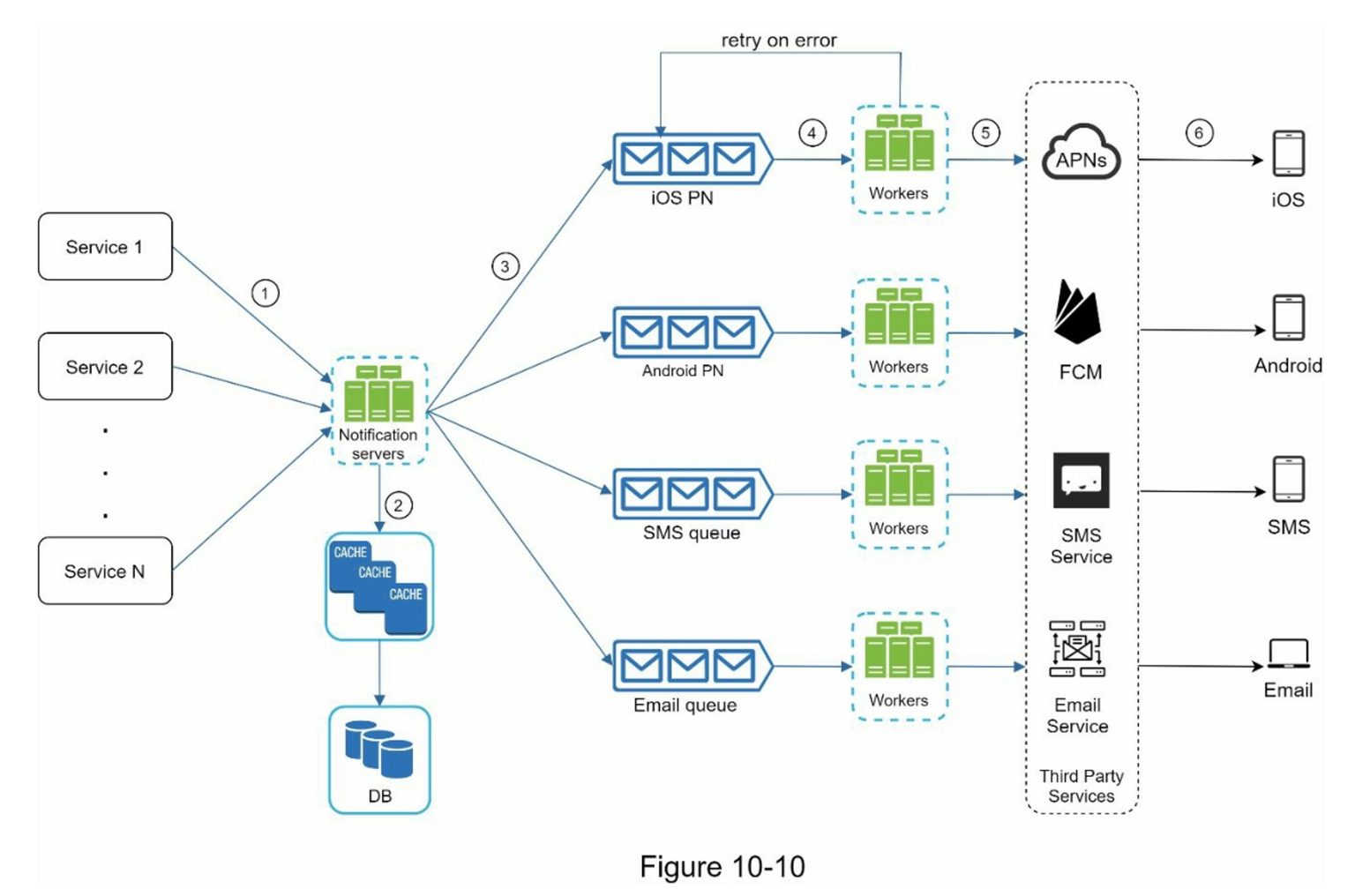
-
Services 1 to N they are different services that send notification events though the API that the Notification Service provides.
-
Notification Service
- Provides API for Services 1 to N to send notification events.
- Simple verification to ensure the notification event is valid.
- Get the data from the database and cache what the notification needs.
- Send the notification to the third-party service.
-
Cache (e.g., User information, Device information, Notification template, etc.)
-
Database (e.g., Uesr, Notification, Config, etc.)
-
Message Queue: Decouple the system components. As buffer to handle the sudden surge in requests.
-
Worker(Consumer): Consume the message from the message queue and send the notification to the third-party service.
-
Third-Party Service
-
User Device
Design Deep Dive
Availability & Reliability
How to prevent data loss?
Most important is to ensure the data cannot be lost.
- Data must be persisted.
- Implement retry mechanism.
Additional Considerations
- Notification Template
- Notification Configuration
- Rate Limiting
- Retry Mechanism
- Security
- Monitoring
- Event Tracking
Updated Design